flowchart LR A[Raw] --> B[SDTM] B[SDTM] --> C[ADaM] C[ADaM] --> D[ARD] D[ARD] --> E[TFL] %% Apply the custom class "highlight" to node B class C highlight; %% Define the style for the "highlight" class: classDef highlight fill:#F9B, stroke:#333, stroke-width:2px;
ADaMs with {admiral} and friends
Objectives
- By the end of this ADaM section you will have:
- Gained an understanding of how to use
admiral,metatools/metacore, andxportrpackages to create ADaMs - Seen code executed to create variables and records common to
ADSLandADVS. - Seen small code snippets of certain functions with play data.
- Checked in on our fav participant - Barb.
- Completed two short exercises using functions from admiral package.
- Gained an understanding of how to use
Play by Play to achieve our Objectives
🕙11:00 - 11:15 Set the Stage: Overview of how we will work, datasets, specs, packages, functions
🕥11:15 - 11:40 Subject-level dataset:
ADSL🕚11:40 - 11:50 Check in on Barb / Exercise
🕦11:50 - 12:20 Basic Data Structure:
ADVS🕚12:20 - 12:30 Check in on Barb / Exercise
🕚12:30 Lunch!
End to End with Barb!!

- We are going to take a glimpse of where Barb is in
ADSLandADVS
Set the Stage
🕥11:00 - 11:15

Set the Stage
- How we will work for the next 90 minutes?
- Data (SDTMs,
ADSL, andADVS) - Specs (Excel document with lots of tabs)
- pharmaverse packages
- playing nice with tidyverse and base R!!
- Functions to make ADaM variables and records.
How we will proceed today?

How we will proceed today?
How we will proceed today continued?
- Two exercises set up to help explore two key functions discussed:
derive_vars_dtm()at end ofADSL.derive_param_computed()at end ofADVS.
- Brief notes on the code in script and exercises:
- Code in scripts should run out of the box.
- You can run now, but if something doesn’t work let’s fix at the exercises.
- Exercises will need some minor updates.
- 3 folks not presenting can help diagnose issues during exercises.
Datasets
ADSL - Subject Level Dataset
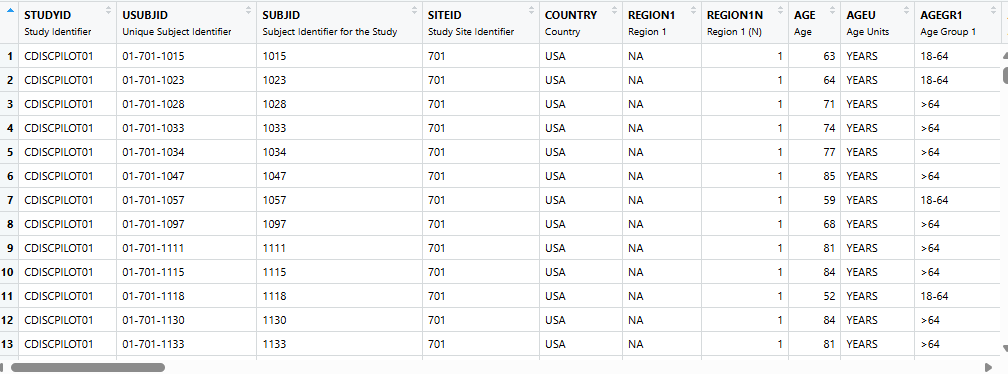
ADSL- Subject Level Dataset, i.e each subject has a record. Focus on adding variables.- We will use SDTM data from the pharmaversesdtm package.
ADSLis available in the pharmaverseadam package
ADVS - Vital Signs Dataset
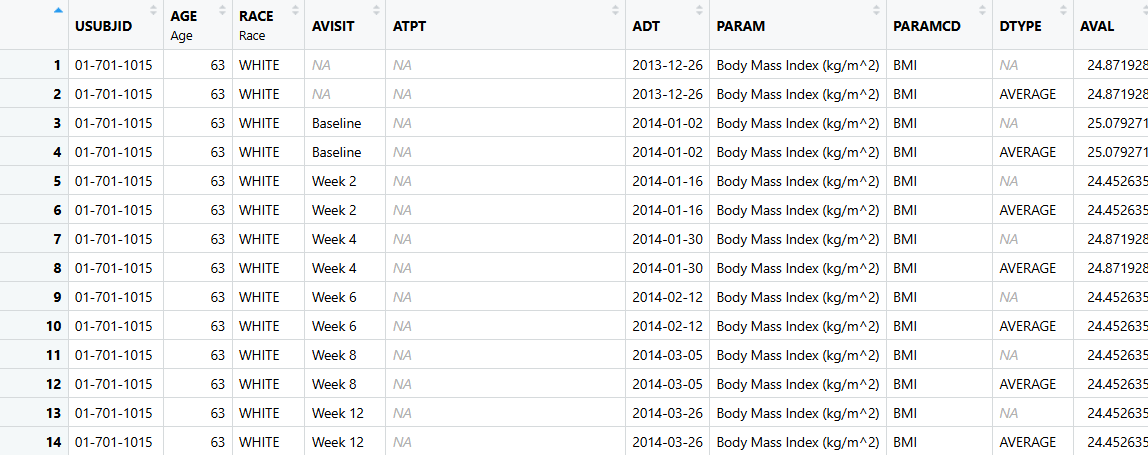
- ADVS - Is a Basic Data Structure (BDS) Dataset. Focus on adding records, but also some variables!
- We will use SDTM data
vsfrom the pharmaversesdtm package andADSLfrom dataset created by theadsl.Rscript. ADVSis available in the pharmaverseadam package
Specs

Spec-details
- Gives specifics on how we derive variables in the ADaMs (extreme traceability)
- P21-like spec
- P21 is spec/data validation tool widely used in the industry for creating and validating SDTMs and ADaMs.
- These specs are not fit for purpose - just a helpful guide
- What is in the the Specs:
- Two datasets, dataset labels and variable keys
- Variables - labels, lengths, types, linked to method
- Codelists / Control Terms!!
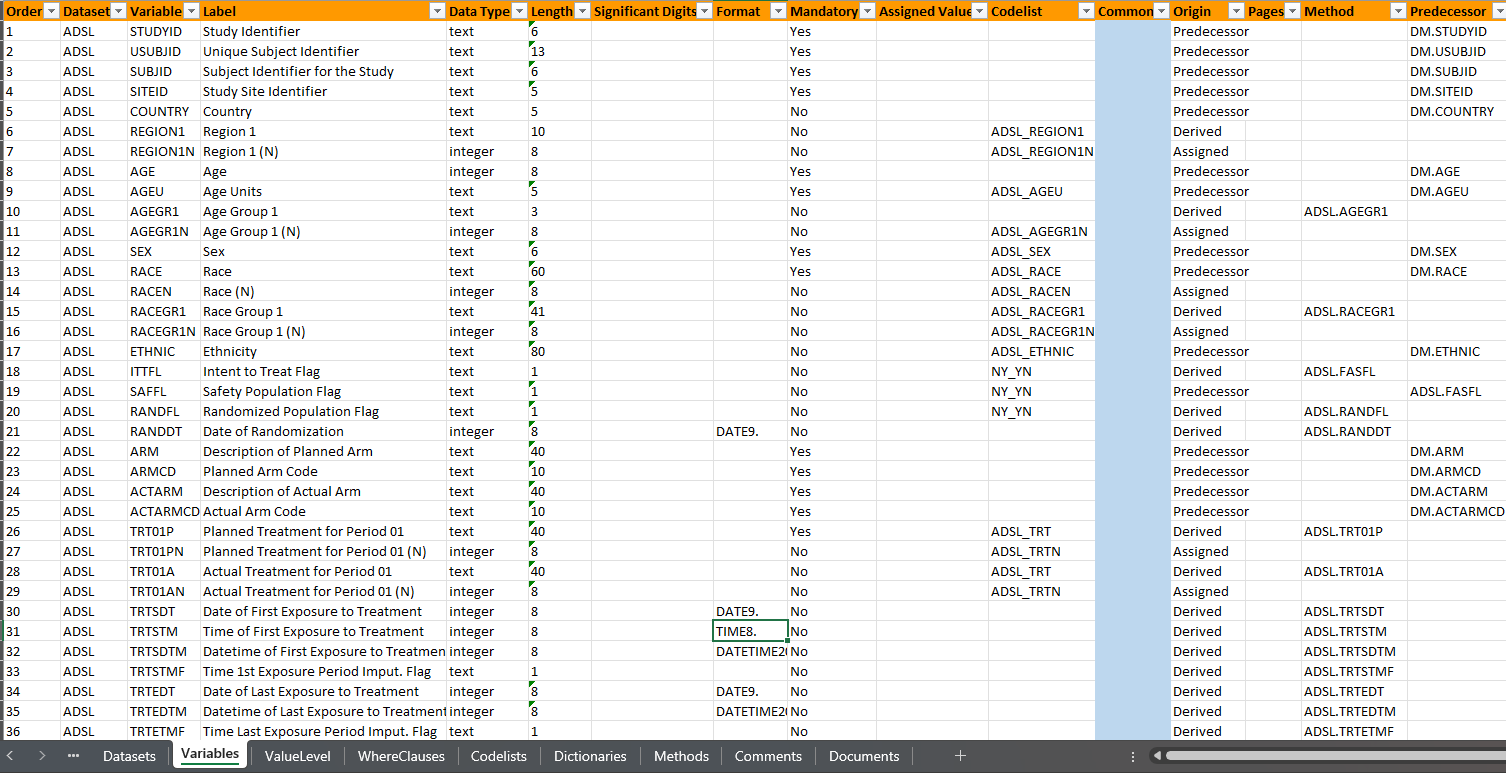
Spec-peek
- Let’s take a quick peek at metadata
The core pharmaverse packages for creating ADaMs

Focus on applying information from our Specs to the ADaMs

Focus on deriving variables and records driven by our Specs

Focus on preparing the dataset as an xpt file to be sent to regulatory agencies.
pharmaverse plays nice!




The ADaM code presented today utilizes all the previously mentioned packages, but also makes use of tidyverse and base R code.
If a function isn’t meeting your needs or looks too cumbersome, then that is okay!
These packages are all modular and play well with others.
admiral
| Package | Function | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| admiral | derive_vars_merged() | left_join on steroids |
| admiral | derive_param_computed() | Core function for wrappers used in ADVS |
| admiral | derive_vars_dy() | Create the relative study day |
| admiral | derive_vars_dtm() | Take a ---DTC variable and turn it into a ---DTM variable |
| admiral | derive_vars_duration() | Duration between timepoints |
| admiral | restrict_derivation() | HOF: Execute a derivation on a subset of the input dataset. |
Most functions in admiral follow these conventions:
var_or_vars_functions add variable(s) to ADaMs_param_functions add records to ADaMs- Other not following this convention typically execute more advanced stuff!!
metacore, metatools and xportr
| Package | Function | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| metacore | spec_to_metacore() | Creates a “special” object from your specs |
| metatools | combine_supp() | Join Parent and Supplementary Datasets |
| metatools | create_var_from_codelist() | Numeric Vars from Specs! |
| metatools | drop_unspec_vars() | Easily drop variables not in Spec |
| xportr | xportr_label() | Apply labels from Spec |
| xportr | xportr_write() | Write out an xpt file |
- Most functions from these packages are about applying metadata from specs to your dataset.
- xportr follows a standard naming convention with
xportr_.
ADSL
🕥 11:15 - 11:40
- Note: Referencing lines in file at each section with a footnote (Lines: ##-##)
The Big Picture of ADSL
- We have an
ADSLscript:
- Using
{pharmaversesdtm}data:dm,suppdm,ex,ae,vs, etc - Uses the
ADSLsection of our spec file - Creating a single record for each subject with a lot of variables.
- 306 observations and 54 variables.
- Write out an xpt file for regulatory send-off!
Reading in our spec for ADSL 1
- Takes a P21-like spec and makes it into an object we can easily access.
where_sep_sheet- option to tell if the information for the dataset is in a separate sheet, like in older p21 specs or in a single sheet like newer p21 specsquietargument should be set toTRUEwhile developing your spec and ADaMs.- Same call in ADVS script.
Combine Parent and Supplementary Data 1
- One line of code to join two datasets: parent and supplementary!
- Supps usually are a collection non-standard data and linking to parent
- Function is from
{metatools}
Let’s turn a --DTC to a *DTM or *DT variable 1
Example from documentation
# A tibble: 7 × 4
MHSTDTC ASTDTM ASTDTF ASTTMF
<chr> <dttm> <chr> <chr>
1 "2019-07-18T15:25:40" 2019-07-18 15:25:40 <NA> <NA>
2 "2019-07-18T15:25" 2019-07-18 15:25:59 <NA> S
3 "2019-07-18" 2019-07-18 23:59:59 <NA> H
4 "2019-02" 2019-02-28 23:59:59 D H
5 "2019" 2019-12-31 23:59:59 M H
6 "2019---07" 2019-12-31 23:59:59 M H
7 "" NA <NA> <NA> Woah…there is more!!
A Simple merge 1
- Filter, arrange, join and rename is a common pattern in ADaMs.
by_varsare going to be the shared variables to connect the two datasets- In admiral, all arguments which can be set to multiple variables, a calculation, or an assignment must be started with
rlang::exprs(). - Check out Programming Concepts and Conventions
Let’s get a more complicated merge 1
order- for each by group the first or last observation from the additional dataset is selected with respect to the specified order.mode- Determines if the first or last observation is selected
Whoa!!! Way more options!!
Let’s derive a Duration Variable 1
Example from documentation
# Derive age in years
data <- tribble(
~USUBJID, ~BRTHDT, ~RANDDT,
"P01", ymd("1984-09-06"), ymd("2020-02-24"),
"P02", ymd("1985-01-01"), NA,
"P03", NA, ymd("2021-03-10"),
"P04", NA, NA
)
derive_vars_duration(data,
new_var = AAGE,
new_var_unit = AAGEU,
start_date = BRTHDT,
end_date = RANDDT,
out_unit = "years",
add_one = FALSE,
trunc_out = TRUE
)# A tibble: 4 × 5
USUBJID BRTHDT RANDDT AAGE AAGEU
<chr> <date> <date> <dbl> <chr>
1 P01 1984-09-06 2020-02-24 35 years
2 P02 1985-01-01 NA NA <NA>
3 P03 NA 2021-03-10 NA <NA>
4 P04 NA NA NA <NA> Ohhh there is more!!
Duration versus Interval
The lubridate package calculates two types of spans between two dates: duration and interval. While these calculations are largely the same, when the unit of the time period is month or year the result can be slightly different.
The difference arises from the ambiguity in the length of “1 month” or “1 year”. Months may have 31, 30, 28, or 29 days, and years are 365 days and 366 during leap years. Durations and intervals help solve the ambiguity in these measures.
Let’s apply Control Terms / Code Lists 1
adsl16 %>%
create_var_from_codelist(adsl_spec, input_var = AGEGR1, out_var = AGEGR1N) %>%
create_var_from_codelist(adsl_spec, input_var = RACE, out_var = RACEN) %>%
create_var_from_codelist(adsl_spec, input_var = RACEGR1, out_var = RACEGR1N) %>%
create_var_from_codelist(adsl_spec, input_var = REGION1, out_var = REGION1N) %>%
create_var_from_codelist(adsl_spec, input_var = TRT01P, out_var = TRT01PN) %>%
create_var_from_codelist(adsl_spec, input_var = TRT01A, out_var = TRT01AN)- Numeric Variables like the above are helpful for sorting options in Tables.
More details
codelist - Optional argument to supply a codelist. Must be a data.frame with code and decode columns such as those created by the function metacore::get_control_term. If no codelist is provided the codelist associated with the column supplied to out_var will be used. By default codelist is NULL.
decode_to_code - Direction of the translation. Default value is TRUE, i.e., assumes the input_var is the decode column of the codelist. Set to FALSE if the input_var is the code column of the codelist.
strict - A logical value indicating whether to perform strict checking against the codelist. If TRUE will issue a warning if values in the input_var column are not present in the codelist. If FALSE no warning is issued and values not present in the codelist will likely result in NA results.
Check in on Barb / Exercise
🕚11:40 - 11:50
Check in on Barb in ADSL

flowchart LR B[SDTM] --> C[ADaM] C[ADaM] --> D[ARDs/TFLs] %% Apply the custom class "highlight" to node B class C highlight; %% Define the style for the "highlight" class: classDef highlight fill:#F9B, stroke:#333, stroke-width:2px;
- USUBJID: 01-701-1034
- SEX: F
- AGE: 77
- RANDDT: 2014-07-01
- TRTSDT: 2014-07-01
- TRTSDTM: 2014-07-01 23:59:59
- TRTEDT: 2014-12-30
- TRTDURD: 183
- EOSDT: 2014-12-30
- EOSSTT: COMPLETED
Check-in Exercise
- Impute the date and time to be last month/day and 23:59:59
- Two arguments to update:
???? - Check out admiral
derive_vars_dtm()documentation
library(tibble)
library(lubridate)
library(admiral)
posit_mh <- tribble(
~USUBJID, ~MHSTDTC,
1, "2019-07-18T15:25:40",
1, "2019-07-18T15:25",
1, "2019-07-18",
2, "2024-02",
2, "2019",
2, "2019---07",
3, ""
)
derive_vars_dtm(
dataset = posit_mh,
new_vars_prefix = "AST",
dtc = MHSTDTC,
highest_imputation = "M",
date_imputation = "????",
time_imputation = "????"
)Check-in Exercise Solution
posit_mh <- tribble(
~USUBJID, ~MHSTDTC,
1, "2019-07-18T15:25:40",
1, "2019-07-18T15:25",
1, "2019-07-18",
2, "2024-02",
2, "2019",
2, "2019---07",
3, ""
)
derive_vars_dtm(
dataset = posit_mh,
new_vars_prefix = "AST",
dtc = MHSTDTC,
highest_imputation = "M",
date_imputation = "last",
time_imputation = "last"
)# A tibble: 7 × 5
USUBJID MHSTDTC ASTDTM ASTDTF ASTTMF
<dbl> <chr> <dttm> <chr> <chr>
1 1 "2019-07-18T15:25:40" 2019-07-18 15:25:40 <NA> <NA>
2 1 "2019-07-18T15:25" 2019-07-18 15:25:59 <NA> S
3 1 "2019-07-18" 2019-07-18 23:59:59 <NA> H
4 2 "2024-02" 2024-02-29 23:59:59 D H
5 2 "2019" 2019-12-31 23:59:59 M H
6 2 "2019---07" 2019-12-31 23:59:59 M H
7 3 "" NA <NA> <NA> ADVS
🕦11:50 - 12:20
- Note: Referencing lines in file at each section with a footnote (Lines: ##-##)
The Big Picture of ADVS
- We have an ADVS script:
- Using
pharmaversesdtmdata:vs - Using the ADVS section of our spec file.
- Creating multiple records for each subject.
- Some
ADSLvariables included. - 60K records and 106 variables.
- Lot’s of functions are repeated within the
ADVSscript used inADSLscript.
- Using
Let’s talk about lookup tables 1
- Moving from
**TEST/**TESTCDtoPARAM/PARAMCD. - More information in the
PARAM/PARAMCD- useful for displays. - Can be used for other lookup tables, e.g. Grading/Toxicity.
A Fuller Look!
Let’s add more records for each subject 1
advs <- advs %>%
derive_param_computed(
by_vars = exprs(STUDYID, USUBJID, VISIT, VISITNUM, ADT, ADY, VSTPT, VSTPTNUM),
parameters = "WEIGHT",
set_values_to = exprs(
AVAL = AVAL.WEIGHT / (AVAL.HEIGHT / 100)^2,
PARAMCD = "BMI",
PARAM = "Body Mass Index (kg/m^2)",
AVALU = "kg/m^2"
),
constant_parameters = c("HEIGHT"),
constant_by_vars = exprs(USUBJID)
)Only two arguments not used!
filter- The specified condition is applied to the input dataset before deriving the new parameter, i.e., only observations fulfilling the condition are taken into account.keep_na- If the argument is set to TRUE, observations are added even if some of the values contributing to the computed value are NA
Let’s derive DTYPE summary records 1
- A DTYPE variable indicates a record within a parameter has been imputed or modified, DTYPE will indicate the method used to populate the analysis value, e.g AVERAGE, MAXIMUM, MINIMUM, LOCF, PHANTOM.
Let’s restrict! 1
- Check out Higher Order Functions for more information.
call_derivation()is super handy if you are doing similar calls with same function, but just changing one or two arguments.
Let’s add a BASE variable 1
- Used to calculate CHG and PCHG variables
Let’s add an Analysis Sequence Variable 1
- ASEQ uniquely indexes records within a subject within an ADaM dataset.
- ASEQ is useful for traceability when the dataset is used as input to another ADaM dataset
check_type- If “message”, “warning” or “error” is specified, the specified message is issued if the observations of the input dataset are not unique with respect to the by variables and the order.
Let’s get that ADaM ready for regulatory agencies 1
- Functions from
{metatools} - Note similar code in
ADSLscript!
Let’s get that data read for regulatory agencies 1
- Functions from
{xportr} - Note similar code in
ADSLscript! domainis needed depending on howmetacoreobject is created.
Check in on Barb / Exercise
🕦 12:20 - 12:30
Check in on Barb in ADVS

flowchart LR B[SDTM] --> C[ADaM] C[ADaM] --> D[ARDs/TFLs] %% Apply the custom class "highlight" to node B class C highlight; %% Define the style for the "highlight" class: classDef highlight fill:#F9B, stroke:#333, stroke-width:2px;
- USUBJID: 01-701-1034
- PARAM/PARAMCD: MAP / Mean Arterial Pressure (mmHg)
- ABLFL/ADT: Y / 2014-07-01
- BASE: 94.33333
- AVIST/ADT: WEEK 2 / 2014-07-15
- AVAL: 115.0
- CHG: 20.6666667
- PCHG: 21.9081272
Check-in Exercise
- We are going to update the function
derive_param_computed()for Mean Arterial Pressure. - Formula: \[ \frac{2DIABP + SYSBP}{3} \]
ADVS <- tribble(
~USUBJID, ~PARAMCD, ~PARAM, ~AVALU, ~AVAL, ~VISIT,
"01-701-1015", "DIABP", "Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg)", "mmHg", 51, "BASELINE",
"01-701-1015", "SYSBP", "Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg)", "mmHg", 121, "BASELINE",
"01-701-1028", "DIABP", "Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg)", "mmHg", 79, "BASELINE",
"01-701-1028", "SYSBP", "Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg)", "mmHg", 130, "BASELINE",
) Check-in Exercise Solution
ADVS <- tribble(
~USUBJID, ~PARAMCD, ~PARAM, ~AVALU, ~AVAL, ~VISIT,
"01-701-1015", "DIABP", "Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg)", "mmHg", 51, "BASELINE",
"01-701-1015", "SYSBP", "Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg)", "mmHg", 121, "BASELINE",
"01-701-1028", "DIABP", "Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg)", "mmHg", 79, "BASELINE",
"01-701-1028", "SYSBP", "Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg)", "mmHg", 130, "BASELINE",
)
derive_param_computed(
ADVS,
by_vars = exprs(USUBJID, VISIT),
parameters = c("SYSBP", "DIABP"),
set_values_to = exprs(
AVAL = (AVAL.SYSBP + 2 * AVAL.DIABP) / 3,
PARAMCD = "MAP",
PARAM = "Mean Arterial Pressure (mmHg)",
AVALU = "mmHg",
)
)# A tibble: 6 × 6
USUBJID PARAMCD PARAM AVALU AVAL VISIT
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 01-701-1015 DIABP Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) mmHg 51 BASELINE
2 01-701-1015 SYSBP Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) mmHg 121 BASELINE
3 01-701-1028 DIABP Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) mmHg 79 BASELINE
4 01-701-1028 SYSBP Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) mmHg 130 BASELINE
5 01-701-1015 MAP Mean Arterial Pressure (mmHg) mmHg 74.3 BASELINE
6 01-701-1028 MAP Mean Arterial Pressure (mmHg) mmHg 96 BASELINEQuestions and Resources
- admiraldiscovery
- pharmaverse examples
- pkgdown sites for xportr, metatools, metacore and admiral
- Extension packages for admiral: admiralophtha, admiralonco, admiralpeds
Closing Thoughts
- Only able to show a small number of
pharmaversepackages and functions today, but please delve deeper to explore the full breadth- If you’d like to contribute to
pharmaverse, check out options at pharmaverse.org- Finally, be sure to join our community on Slack!
Packages and Session Information
R version 4.5.1 (2025-06-13)
Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
Running under: Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/openblas-pthread/libblas.so.3
LAPACK: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/openblas-pthread/libopenblasp-r0.3.26.so; LAPACK version 3.12.0
locale:
[1] LC_CTYPE=C.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C LC_TIME=C.UTF-8
[4] LC_COLLATE=C.UTF-8 LC_MONETARY=C.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=C.UTF-8
[7] LC_PAPER=C.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C LC_ADDRESS=C
[10] LC_TELEPHONE=C LC_MEASUREMENT=C.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C
time zone: UTC
tzcode source: system (glibc)
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices datasets utils methods base
other attached packages:
[1] lubridate_1.9.4 admiral_1.3.1 tibble_3.3.0 countdown_0.4.0
[5] glue_1.8.0
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] jsonlite_2.0.0 dplyr_1.1.4 compiler_4.5.1 renv_1.1.5
[5] tidyselect_1.2.1 xml2_1.3.8 stringr_1.5.1 tidyr_1.3.1
[9] yaml_2.3.10 fastmap_1.2.0 R6_2.6.1 generics_0.1.4
[13] admiraldev_1.3.1 knitr_1.50 pillar_1.11.0 rlang_1.1.6
[17] utf8_1.2.6 stringi_1.8.7 roxygen2_7.3.2 xfun_0.52
[21] timechange_0.3.0 cli_3.6.5 withr_3.0.2 magrittr_2.0.3
[25] digest_0.6.37 hms_1.1.3 lifecycle_1.0.4 vctrs_0.6.5
[29] evaluate_1.0.4 rmarkdown_2.29 purrr_1.1.0 tools_4.5.1
[33] pkgconfig_2.0.3 htmltools_0.5.8.1